Determining the particle concentration of PIT nanoemulsions
In a feasibility study with Henkel, we tested two innovative emulsion types to better understand their composition.
The results revealed significant differences between the samples.

Challenge
Phase inversion is an important industrial process to make stable emulsions e.g. for personal care products. After phase inversion, the liquid-in-liquid dispersions have a droplet size in the nano-range. This brings a number of benefits due to e.g. high surface area per volume, high stability and other desirable properties.
However, it is not always easy to control and predict the final droplet size during the production process.
Application highlights
During measurement the live datastream of particles already gave an indication of differences between the two samples.
The number of particles (shown as strips of light) passing through the measuring cell was noticeably lower for Emulsion 1 than for Emulsion 2 (see Figure 1).
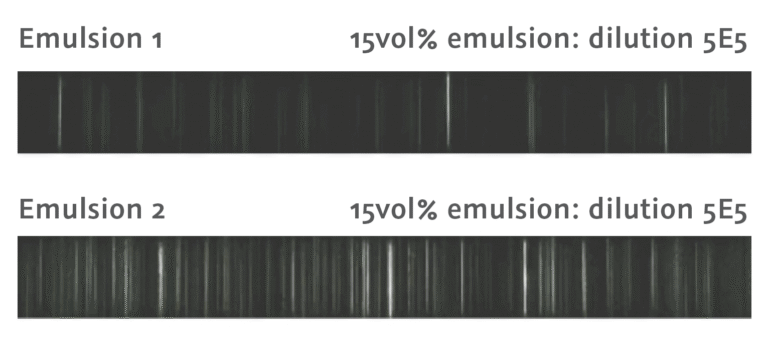
Fig. 1: Comparison of the live datastreams of Emulsion 1 (above) and Emulsion 2 (below) showing noticeably more particles passing through the cell during measurement of Emulsion 2
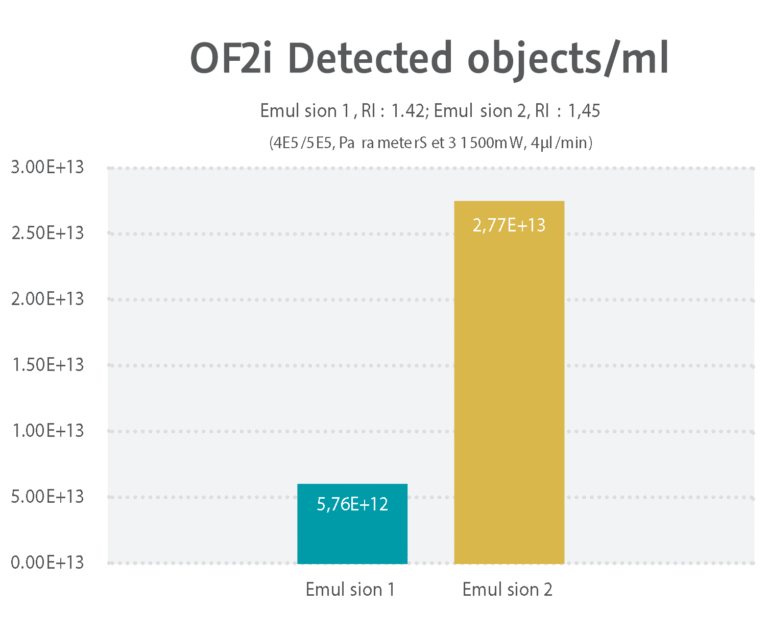
Fig. 2: Results of the OF2i® measurement of object concentration on Emulsion 1 and Emulsion 2
Results
Subsequent comparison of the OF2i® data for both samples revealed that the object concentration (number of objects) of Emulsion 2 was 4.8 times higher than for Emulsion 1 (see Figure 2).
Configuration of the setup:
BRAVE B-Curious device with BRAVE B-Aware software module for particle sizing, Fluid Automation Module, Control and Evaluation Module and software
The analysis setup used in this case
The BRAVE B-Curious particle analyzer with BRAVE B-Aware software module.
The BRAVE B-Aware module detects and tracks very small particles (from 5 nm) and delivers particle counts and particle concentration values.
Ideal for detecting the onset of aggregation and tracking sample behavior when very small particles are involved.
Continuous in-flow measurement.
Detection range
5 nm* to 50 nm* (*sample-dependent)
Concentration range
Sample-dependent
Particles detected per minute
Over 1000 particles per minute (sample-dependent)


